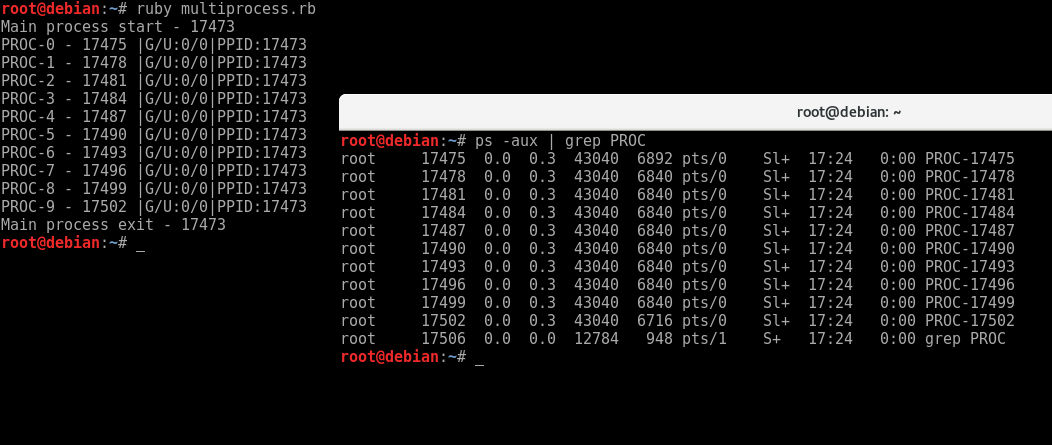
关于多线程与多进程的区别此处就不再赘述了。
Python3中已经具备了非常完善的多线程与多进程的相关库,可以非常容易的实现程序多进程与多线程的功能。
示例代码如下:
多线程示例
multithread.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
import os
import time
import threading
def test_proc(name):
print( "Run child process %s(%s)" % (name,os.getpid()) )
time.sleep(10)
class MultiThread( threading.Thread ):
def __init__(self,thread_name):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.thread_name = thread_name
def run(self):
test_proc("test")
threads = []
for i in range(1,10):
thread = MultiThread( "Thread-%s" % i )
thread.start()
threads.append( thread )
for t in threads:
t.join()
|
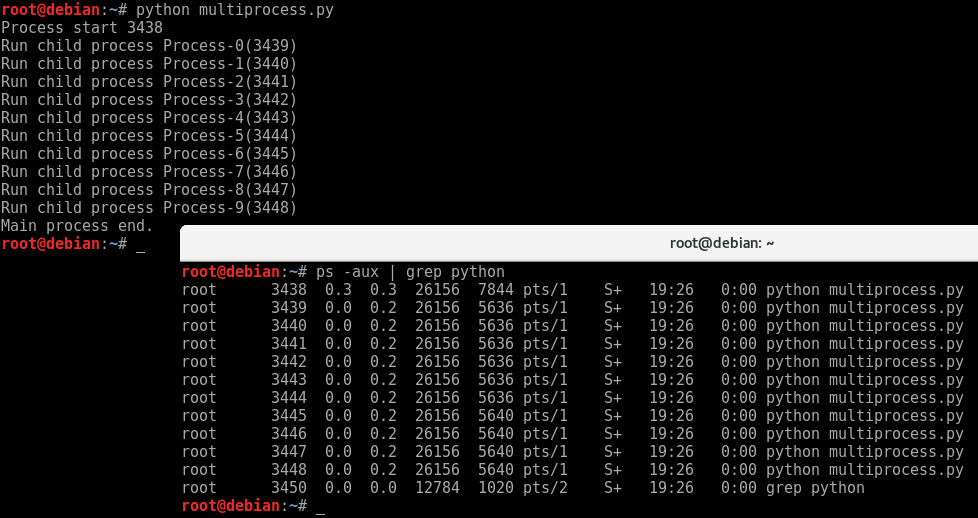
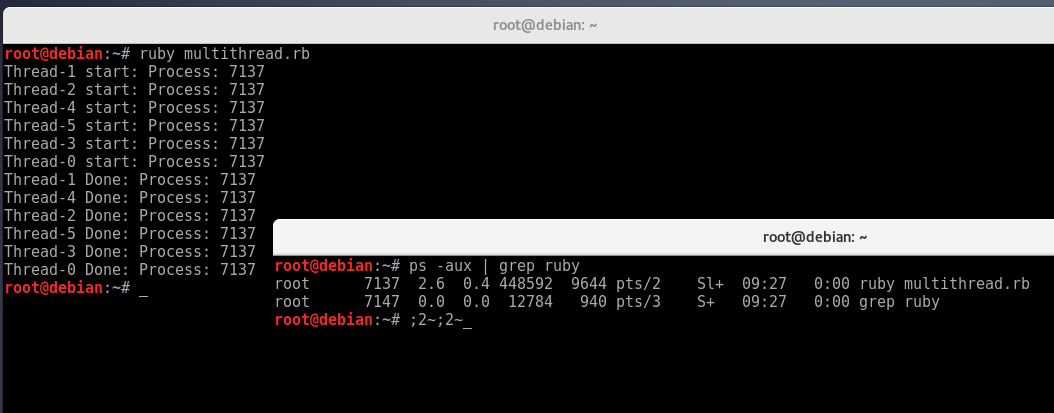
运行结果:
多进程示例
multiprocess.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
import os
import time
import multiprocessing
def test_proc(name):
print( "Run child process %s(%s)" % (name,os.getpid()) )
time.sleep(10)
if __name__=="__main__":
print("Process start %s" % os.getpid())
processes = []
for i in range( 0, 10):
p=multiprocessing.Process( target=test_proc, args=("Process-%s" % i,) )
p.start()
processes.append(p)
for p in processes:
p.join()
print( "Main process end.")
|
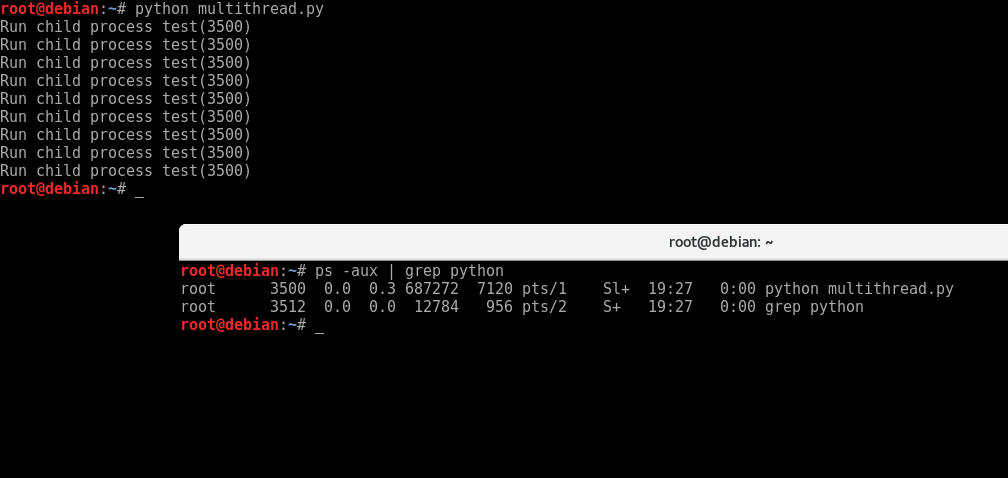
运行结果: